The “Specified Skilled Worker (SSW) or 特定技能 (Tokutei Ginou)” status of residence (visa type) was introduced in the hopes of drawing skilled workers to Japan. The “Specified Skilled Worker” status of residence (visa type) is divided into Types 1 and 2. At the moment, there are 12 industries with various occupations that are eligible for SSW.
Learn all you need to know about “Tokutei Ginou” including requirements, the current status of SSW in Japan, the quota for SSW visas, and the 4 new industries to be added.
First Published: 2021-01-13
Updated: 2024-04-24
Table of Contents
- What is the “Tokutei Ginou / Specified Skilled Worker” visa?
- The 2 Types of Tokutei Ginou / SSW Visa
- Eligible Industries and Special Skills Test for Tokutei Ginou / SSW Visa
- How to Apply for Tokutei Ginou / SSW Visa
- Current Status of SSW in Japan (as of December 2023)
- Find a Specific Skills Job in Japan with Leverages Global Support
 Are you having any issues with job-hunting in Japan?
Are you having any issues with job-hunting in Japan?
What is the “Tokutei Ginou / Specified Skilled Worker” visa?

The “Tokutei Ginou (特定技能) Specified Skilled Worker (SSW)” is a new status of residence (visa type) target 12 specific industries that was introduced in April 2019 to alleviate Japan’s labour shortages. This status of residence (visa type) allows foreign nationals to work simple labour industry jobs.
Specific Work (12 Industries)
- Nursing Care
- Building Cleaning Management
- Machine Parts and Tooling / Industrial Machinery / Electric / Electronic Information
- Construction
- Shipbuilding and Ship Machinery
- Automobile Repair and Maintenance
- Aviation
- Accommodation
- Agriculture
- Fishery and Aquaculture
- Manufacture of Food and Beverages
- Food Service
[Reference] The similar sounding “Tokutei Katsudou (特定活動)” is actually a different type of status of residence (visa type) called the “Designated Activities” visa. International students who graduated from a Japanese university, and work in manufacturing, restaurant services, or nursing care can apply for a “Designated Activities” visa. Read more about the “Designated Activities” visa here.
Writer's Pick
The 2 Types of Tokutei Ginou / SSW Visa
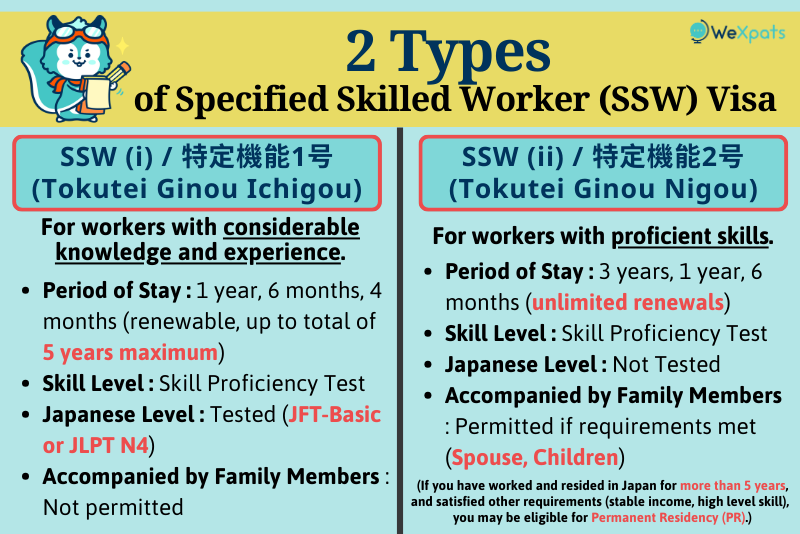
Japan’s Tokutei Ginou SSW visa is broadly divided into:
- SSW (i) (特定機能1号, Tokutei Ginou Ichigou) - refers to workers with considerable knowledge and experience in one of the 12 industries
- SSW (ii) (特定機能2号, Tokutei Ginou Nigou) - refers to workers with proficient skills in one of 11 industries excluding nursing care
There are differences between periods of stay, and whether family members can accompany during stay depending on which type.
SSW (i) - 特定機能1号 (Tokutei Ginou Ichigou)
This status of residence (visa type) is for foreign nationals that are engaged in skilled work in a specific industry (12 fields) that requires considerable knowledge and experience.
Features of SSW (i)
- Period of Stay: 1 year, 6 months, 4 months (renewable up to maximum of 5 years in total)
- Skill Level: Tested by skills proficiency test for each specified industry, etc. (exempted for those who have completed the training programme for Technical Intern Training (ii), etc.)
- Japanese Language Proficiency: Tested by exam (sufficient Japanese proficiency for daily life and workplace communication - around JLPT N4 level)
- Accompanied by Family Members: Not permitted.
- Application can be done through accepting organisations or registered support organisations.
[Reference] What is the Technical Intern Training Programme?
The Technical Intern Training Programme was established to transfer skills and technical knowledge and cooperate in nurturing talent who will be responsible for the economic development of developing countries.
The target countries (India, Indonesia, Uzbekistan, Cambodia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, China, Nepal, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Philippines, Vietnam, Peru, Myanmar, Mongolia, and Laos) and Japan have entered into bilateral agreements. As of October 31, 2023, a total of 165 jobs in 90 occupations are targeted.
There are many things in common with SSW in terms of industry, occupation (jobs), and skills test. It is common for technical interns to apply for a SSW status of residence (visa) in order to continue working in Japan.
※ MHLW, “技能実習制度 移行対象職種・作業一覧(90職種165作業)” [2023.10.31] PDF ※ JITCO, “What is the Technical Intern Training Program?”
SSW (ii) - 特定機能2号 (Tokutei Ginou Nigou)
This status of residence (visa type) is for foreign nationals that are engaged in skilled work that requires proficient skills. From August 2023, the scope of SSW (ii) was expanded to 11 specific industries, excluding nursing care.
[Reference] “Nursing Care” is excluded from SSW (ii) because there is already a “Nursing Care (介護, Kaigo)” status of residence (visa type) that was implemented in 2017 to address the shortage of care workers in Japan. The “Nursing Care” visa is only eligible for Certified Care Workers. Read about how to become a Certified Care Worker in Japan here.
Features of SSW (ii)
- Period of Stay: 3 years, 1 year, 6 months (unlimited renewals; if you have worked and reside in Japan for more than 5 years, you may be eligible for permanent residency - provided conditions such as proof of stable income and employment, and high level of skill acquisition are met)
- Skill Level: Tested by skills proficiency test for each specified industry, etc. (operational guidelines are policies for each field can be checked here)
- Japanese Language Proficiency: Not Tested
- Accompanied by Family Members: Available if requirements are met (spouse, children)
- Ineligible for application through accepting organisations or registered support organisations.
Given the new trends in the Japanese job market for foreign nationals, it's important to pay attention to the latest available options if you're considering working in Japan.
For more detailed information, please visit the Support Website for the Specified Skilled Worker Program (operated by Immigration Services Agency of Japan).
Eligible Industries and Special Skills Test for Tokutei Ginou / SSW Visa

We have gone through the two types of “Tokutei Ginou SSW” status of residence (visa types) there are. Next, let’s take a closer look at the specified industries and occupations that are eligible for SSW to work in. This also relates to the content of the skills proficiency test that is required to obtain a SSW visa.
Nursing Care / 介護 (Kaigo) - [1 Test Category]
Physical care (such as assistance with bathing, feeding and excretion, etc. according to the user’s mental and physical conditions), as well as accompanying support services (such as conducting recreational activities, assisting with functional training, etc.).
However, home visit nursing care services are excluded from the SSW visa.
Building Cleaning / ビルクリーニング (Biru Kuri-ningu) - [1 Test Category]
Interior cleaning of buildings.
Machine Parts and Tooling (素形材, Sokeizai) / Industrial Machinery (産業機械, Sangyou Kikai) / Electric (電気, Denki) / Electronic Information (電子情報関連製造業, Denshijouhou Kanren Seizougyou) - [19 Test Categories]
Casting (鋳造, Chuuzou), Forging (鍛造, Tanzou), Painting, Finishing (仕上げ, Shiage), Electrical Equipment Assembly, Welding, Forging, Ironworking, Machinery Inspection (機械検査, Kikai Kensa), Machinery Maintenance (機械保全, Kikai Hozen), Machining (機械加工, Kikai Kakou), Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing, Industrial Packaging, Die Casting, Factory Sheet Metal Work, Plastic Moulding, Plating, Metal Pressing, and Aluminium Anodising Treatment.
Construction / 建設 (Kensetsu) - [18 Test Categories]
Formwork Construction, Earthwork, Interior Finishing / Mounting, Thermal Insulation (Heat Insulation / Cold Insulation), Plastering, Roofing (屋根ふき, Yanefuki), Scaffolding (とび, Tobi), Spray Polyurethane Foam (吹付ウレタン, Fukitsuke Uretan), Concrete Pumping, Telecommunications, Carpentry (大工, Daiku), Offshore Civil Engineering, Tunnelling, Reinforcement Construction, Piping, Construction Machinery Installation, Reinforcing Bar Joints, and Sheet Metal Work.
Shipbuilding (造船, Zousen) / Ship Machinery (Hakuyou Kougyou) - [6 Test Categories]
Welding, Finishing, Painting, Machining, Ironworking, and Electrical Equipment Assembly.
Automobile Repair and Maintenance (自動車整備, Jidoushaseibi) - [1 Test Category]
Automobile routine maintenance, period maintenance, disassembly maintenance.
Aviation (航空, Koukuu) - [2 Test Categories]
Airport Ground Handling (such as ground movement support, baggage & cargo handling, etc.), and Aircraft Maintenance (such as maintenance for aircraft body, equipment, etc.)
Accommodation (宿泊, Shukuhaku) - [1 Test Category]
Providing accommodation services such as front desk, planning & public relations, customer service, and restaurant services)
Agriculture (農業, Nougyou) - [2 Test Categories]
General Crop Farming (such as crop management, handling of agricultural products, etc.), and General Livestock Farming (such as feeding management, handling of livestock products, etc.).
Fishery (漁業, Gyogyou) - [2 Test Categories]
Fishery (such as manufacturing & repair of fishing gear, discovery of aquatic animals and plants, operation of fishing gear & fishing machinery, collection of aquatic animals and plants, processing/storing/ensuring safety and health of catch, etc.), and Aquaculture (such as production/repair/management of aquaculture material, breeding management/harvest/processing/ensuring safety and hygiene of aquaculture animals and plants, etc.).
Manufacture of Food and Beverages (飲食料品製造業, Inshokuryouhin Seizougyou) - [1 Test Category]
General Manufacturing of Food and Beverages (excluding liquor) including processing and safety & hygiene.
Food Service (外食業, Gaishokugyou) - [1 Test Category]
General Food Service (such as food & drink preparation, customer service, store management).
※ MOFA, “SSW” ※ MOJ, “特定機能:特定産業分野と受入れ見込数等” Page 3
[Breaking News] Cabinet Decision to Add 4 Fields of “Specified Skills”
Currently, there are a total of 12 specified industries that are eligible for the Tokutei Ginou SSW (i), but at a recent cabinet meeting just last month, it was decided that 4 new industries will be added.
- Automobile Transportation Industry (自動車運送業, Jidousha Unsougyou): taxi drivers, bus drivers, truck drivers, etc.
- Railway (鉄道, Tetsudou): train drivers and conductors, station staff, vehicle/tracks/electrical system maintenance, etc.
- Lumber Industry (木材産業, Mokuzai Sangyou)
- Forestry (林業, Ringyou)
Preparations for the skills proficiency tests (for the above new industries) will begin this month, along with the revision of the law.
Industry-specific “Skills Proficiency Test” and Japanese Language Proficiency Test “JFT-Basic”
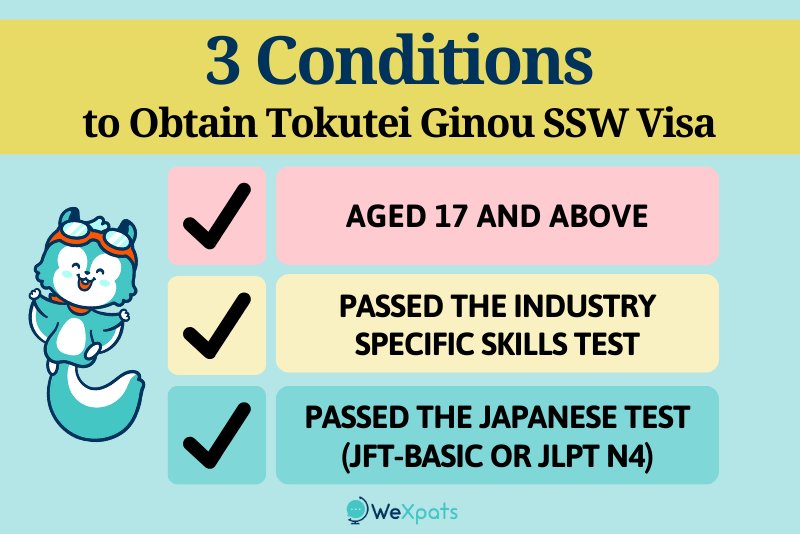
Individuals aged 17 and above who have passed the industry-specific skills proficiency test and the Japanese language proficiency test (JFT-Basic or JLPT N4) can obtain a Tokutei Ginou SSW visa. There are no other specific educational requirements.
The skills proficiency test and Japanese language proficiency test are the 2 most important conditions when applying for a Tokutei Ginou SSW visa. The skills proficiency test is conducted for each industry field, this means that you must take the test prepared for the industry you intend to work in. The skills proficiency test includes practical and essential knowledge related to the selected job.
- Skills Proficiency Test: The skills proficiency test is conducted either in Japan or a foreign country where the test is administered (the administering country varies by industry, administering countries include the Philippines, Cambodia, Indonesia, Thailand, India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and more). From April 1, 2020, individuals can enter Japan on a “short-term stay” visa (such as a tourist visa) to take the test.
- Japanese Language Proficiency Test: Japanese language proficiency is measured by the JFT-Basic (Japan Foundation Test for Basic Japanese), which assesses the ability of foreign nationals coming to Japan for employment to communicate in daily life situations. JFT-Basic tests are conducted 6 times a year in administering countries (such as India, Indonesia, Myanmar, Nepal, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, etc.). There is only 1 level.
If the JFT-Basic test is not available in your country, you can obtain the JLPT (Japanese Language Proficiency Test) N4 or higher. For the nursing care industry, there is a separate test called the “Nursing Care Japanese Language Test (介護日本語評価試験, Kaigo Nihongo Hyouka Shiken)”.
Both the JFT-Basic and Skills Proficiency Tests are usually conducted as computer-based tests unless there is a practical exam requirement. Those who have completed the Technical Intern Training Programme are exempted from the Japanese language proficiency test, and only need to take the skills proficiency test.
※ ISA, “試験関係: 技能試験” ※ JFT-Basic, “JFT-Basicとは” (English site available)
[Example] Food Service Industry-Specific Skills Proficiency Test
The domestic industry-specific skills proficiency test can be taken by those who are “residing in Japan with a status of residence at the time of taking the test”, and those on a tourist visa can also take the test with a “status of residence: short-term stay”.
Tests are largely divided into a “Industry-specific Skills Proficiency Test” and a “Japanese Language Proficiency Test”. The “Industry-specific Skills Proficiency Test” is further divided into a “written test” and a “practical test”.
Below, we will show an example of what an industry-specific skills proficiency test looks like. For the SSW (i) Food Service Industry (外食業, Gaishokugyou), the test content is as follows:
(For reference purposes, the SSW (ii) Food Service Industry test has an additional examinable category for “Store Management”.)
Written Test
|
Categories |
Content |
Questions |
Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Hygiene Control |
・Knowledge of Basic Hygiene Control |
10 Questions |
Full Score: 40 points |
|
Preparation of |
・Knowledge of Raw Ingredients |
10 Questions |
Full Score: 30 points |
|
Customer Service |
・Knowledge of Customer Services |
10 Questions |
Full Score: 30 points |
(Total 30 Questions, 100 Points out of 100)
Practical Test
The practical test consists of 2 types of questions - “Judgement Test” and “Plan Formulation”. The Judgement Test evaluates the ability to make decisions based on theoretical knowledge and practical scenarios, while the Plan Formulation assesses the ability to develop plans or strategies based on understanding of the subject matter and its practical applications.
The tested categories and content is the same as for the written test. Each category consists of 3 Judgement Test questions and 2 Plan Formulation questions.
|
Categories |
Content |
Questions |
Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Hygiene Control |
・Knowledge of Basic Hygiene Control |
J: 3 / P: 2 |
Full Score: 40 points |
|
Preparation of |
・Knowledge of Raw Ingredients |
J: 3 / P: 2 |
Full Score: 30 points |
|
Customer Service |
・Knowledge of Customer Services |
J: 3 / P: 2 |
Full Score: 30 points |
(Total 15 Questions, 100 Points out of 100)
※ OTAFF, "外食業特定技能1号技能測定試験ー国内試験案内" PDF
The passing score is 65 out of 100.
The study material for the Food Service Industry-specific Skills Proficiency Test is available to download on the Japan Food Service Association's website here. They are available in 8 languages including Japanese and English. Download the PDFs and use them to prepare for the test.
The test fee is 7,000 Yen.
Skills Proficiency Test are usually held 3 times a year. For the Food Service Industry, the schedule of testing in Japan is as follows:
|
Test |
Registration |
Results |
|---|---|---|
|
May |
April |
July |
|
October |
August |
November |
|
January |
November |
February |
For more detailed information about the test schedule, please visit the OTAFF website.
[Note] After passing the SSW tests, you will need to separately apply for, or change, your status of residence. Once you obtain the SSW (i) status of residence (visa type), you can renew it every 1 year, 6 months, or 4 months, up to a total of 5 years.
How to Apply for Tokutei Ginou / SSW Visa

Upon satisfying the conditions for a SSW visa, namely passing the industry-specific skills test and Japanese language proficiency test, your employer can apply for a “Certificate of Eligibility (在留資格認定証明書)”. After receiving the Certificate of Eligibility (usually 1~3 months from application), forward it to the Japanese embassy or consulate in your home country to apply for a visa. Once you have obtained your visa, you may now enter Japan to work as a Specified Skilled Worker.
Before starting work, Specified Skilled Workers can participate in orientation sessions provided by Registered Support Organisations (登録支援機関, Touroku Shien Kikan) in Japan to adapt to life in Japan. They can also receive assistance with tasks such as opening a bank account, purchasing a mobile phone, and Japanese interpretation.
Specified Skilled Workers are entitled to receive the same level of compensation as Japanese workers in the same workplace. They are also entitled to paid leave and other employee benefits.
We recommend reading the information contained in the links below to learn what rights you are entitled to.
※ JITCO, “What is a "Specified Skilled Worker" Residency Status?” ※ JETRO, “4.5 Legislation on working hours, breaks and days off”
Current Status of SSW in Japan (as of December 2023)

As at the end of December 2023, the total number of Specified Skilled Workers in Japan was 208,462, of which 37 are SSW (ii) visa-holders.
Number of Specified Skilled Workers by Country
|
Country |
No. of People [SSW (i)] |
No. of People [SSW (ii)] |
|---|---|---|
|
Vietnam |
110,628 (53.1%) |
20 |
|
Indonesia |
34,253 (16.4%) |
2 |
|
The Philippines |
21,364 (10.3%) |
3 |
|
China |
13,456 (6.5%) |
12 |
|
Myanmar |
11,873 (5.7%) |
0 |
|
Cambodia |
4,664 (2.2%) |
0 |
|
Nepal |
2,282 (2.1%) |
0 |
|
Thailand |
4,359 (2.1%) |
0 |
|
Others |
984 (1.6%) |
0 |
Number of Specified Skilled Workers by Specific Industry
|
Industry |
No. of People [SSW (i)] |
No. of People [SSW (ii)] |
|---|---|---|
|
Manufacturing of Food |
61,095 (29.3%) |
0 |
|
Machine Parts and Tooling / |
40,069 (19.2%) |
1 |
|
Nursing Care |
28,400 (13.6%) |
0 |
|
Construction |
24,433 (11.7%) |
30 |
|
Agriculture |
23,861 (11.4%) |
0 |
|
Food Service |
13,312 (6.4%) |
0 |
|
Others |
17,255 (8.3%) |
6 |
Number of Specified Skilled Workers by Prefecture
|
Prefecture |
No. of People [SSW (i)] |
No. of People [SSW (ii)] |
|---|---|---|
|
Aichi |
17,632 |
3 |
|
Osaka |
13,275 |
3 |
|
Saitama |
12,396 |
6 |
|
Chiba |
12,293 |
1 |
|
Tokyo |
11,360 |
5 |
|
Ibaraki |
11,300 |
0 |
|
Kanagawa |
10,829 |
2 |
|
Hokkaido |
8,297 |
0 |
|
Fukuoka |
7,670 |
2 |
|
Hyogo |
7,619 |
0 |
|
Hiroshima |
7,566 |
3 |
|
Gunma |
6,655 |
0 |
|
Shizuoka |
6,503 |
0 |
|
Gifu |
5,075 |
3 |
|
Others |
Less than 5,000 |
9 |
※ ISA, “特定技能在留外国人数の公表等 - 特定技能在留外国人数 令和5年12月末”
Significant Increase of Applications to Change Status of Residence to “Specified Skilled Worker”
The graph below shows the number of people working in Japan on a SSW visa from April 2019 to the end of December 2023.
As illustrated in the graph, the orange are people who applied for a SSW visa from their country before entering Japan, while the green are people who were residing in Japan on a different status of residence (visa type) and changed to SSW visa.
You can see that the number of people changing their status of residence (visa type) to SSW visa is increasing.
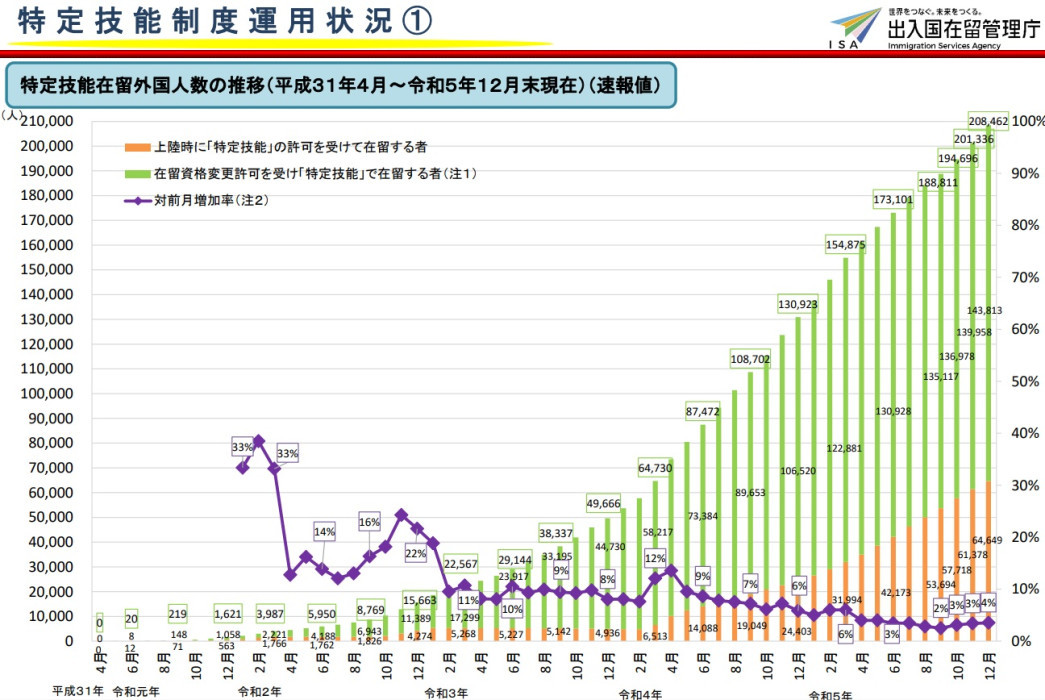
Image from ISA.
Find a Specific Skills Job in Japan with Leverages Global Support

Leverages Global Support is a career support service that introduces jobs that require specific skills to specified skilled workers.
We also help with all the procedures required for employment and job changes, such as change of status of residence (visa type) and interview practice. If you have any problems after starting work, please feel free to contact us as well.
If you would like to know more about specified skilled workers and specific skills, please read this article, or contact a career advisor.
Recommended For
- Specified Skilled Workers who are thinking about changing jobs
- Technical Interns who want to switch to becoming a Specified Skilled Worker (You can try working in a new industry even with no experience!)
- International Students who have graduated from a Japanese school but are having trouble finding a job
How to Use Leverages Global Support
Ask for Job Recommendations
A career advisor will support you with your job search based on your desires. If you would like to be introduced to a specific skill job, feel free to send us a message using the link below.
Mention “WeXpatsを見た” at the beginning of your message, and our staff will respond promptly.
※ A Facebook account is required. Responses will be in Japanese.
Browse Jobs Yourself
You can search for the perfect job by specifying your Japanese level, occupation, work location, etc. We have many jobs available not only for Specified Skilled Workers, but also for Engineer / Specialist in Humanities / International Services.
※ You can register from outside Japan, but only those living in Japan can apply for jobs.


































